SCS
0.0200

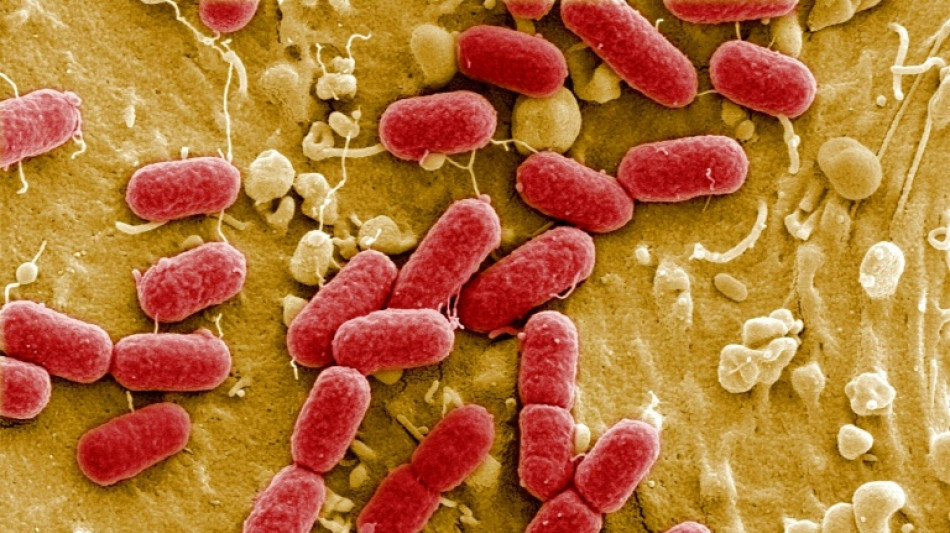
Infections of drug-resistant superbugs are projected to kill nearly 40 million people over the next 25 years, a global analysis predicted on Monday, as the researchers called for action to avoid this grim scenario.
Superbugs -- strains of bacteria or pathogens that have become resistant to antibiotics, making them much harder to treat -- have been recognised as a rising threat to global health.
The analysis has been billed as the first research to track the global impact of superbugs over time, and estimate what could happen next.
More than a million people died from the superbugs -- also called antimicrobial resistance (AMR) -- a year across the world between 1990 and 2021, according to the study in The Lancet journal.
Deaths among children under five from superbugs actually fell by more than 50 percent over the last three decades, the study said, due to improving measures to prevent and control infections for infants.
However when children now catch superbugs, the infections are much harder to treat.
And deaths of over-70s have surged by more than 80 percent over the same period, as an ageing population became more vulnerable to infection.
Deaths from infections of MRSA, a type of staph bacteria that has become resistant to many antibiotics, doubled to 130,000 in 2021 from three decades earlier, the study said.
- 'This threat is growing' -
The researchers used modelling to estimate that -- based on current trends -- the number of direct deaths from AMR would rise by 67 percent to reach nearly two million a year by 2050.
It will also play a role in a further 8.2 million annual deaths, a jump of nearly 75 percent, according to the modelling.
Under this scenario, AMR will have directly killed 39 million people over the next quarter century, and contributed to a total of 169 million deaths, it added.
But less dire scenarios are also possible.
If the world works to improve care for severe infections and access to antimicrobial drugs, it could save the lives of 92 million people by 2050, the modelling suggested.
"These findings highlight that AMR has been a significant global health threat for decades and that this threat is growing," study co-author Mohsen Naghavi of the US-based Institute of Health Metrics said in a statement.
The researchers looked at 22 pathogens, 84 combinations of drugs and pathogens, and 11 infectious syndromes such as meningitis. The study involved data from 520 million individual records across 204 countries and territories.
It was released ahead of a high-level AMR meeting at the United Nations scheduled for September 26.
Antimicrobial resistance is a natural phenomenon, but the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in humans, animals and plants has made the problem worse.
P.Benes--TPP