RBGPF
0.0000

Lucy Akinyi's three children were infected with malaria so often she would be at their local health clinic in western Kenya every other week getting them treated.
When offered the chance to protect her children with the world's first vaccine against the deadly parasitic disease, Akinyi jumped at the chance.
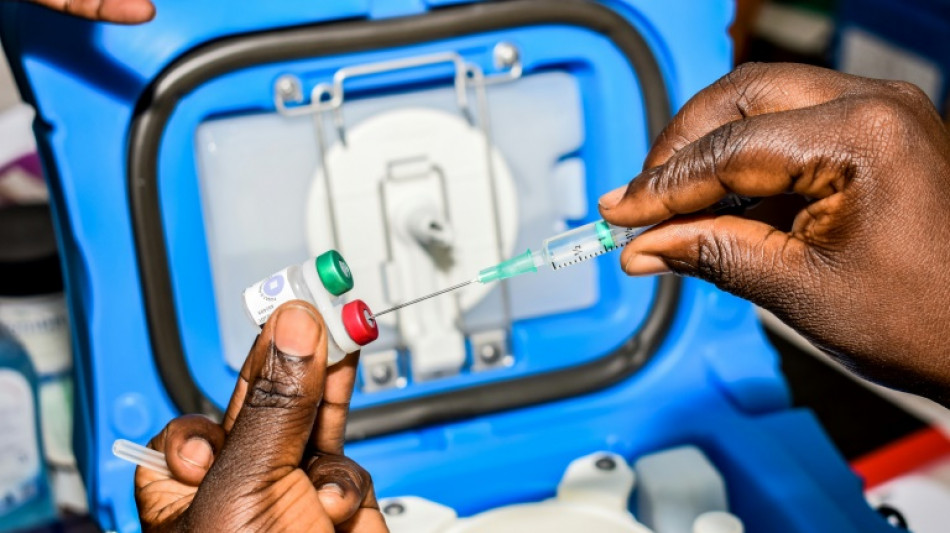
More than 100,000 children in malaria-endemic western Kenya have received the new vaccine against the disease, which kills 260,000 children under five every year in sub-Saharan Africa.
A pilot programme has been rolling out the groundbreaking drug -- which was 30 years in the making -- in Kenya, Ghana and Malawi since 2019.
It was approved for broad use for children in sub-Saharan Africa and other at-risk regions by the World Health Organization (WHO) in October last year.
For Akinyi and her extended family, the vaccine has worked wonders.
She would always place mosquito nets over her children while they slept, but despite her best efforts they would still get bitten outside while playing.
"We used to have a lot of malaria in our home. We could be at the hospital three times in a month," Akinyi said.
But none of her children have tested positive for malaria since being vaccinated, she said, bringing her great comfort living in a region where the disease is a major killer.
"We are very happy because none of our children are sick," Akinyi said.
Her sister-in-law, Millicent Akoth Oyoya, decided to get her own children jabbed after seeing the benefit it brought her nieces and nephews.
"When she (Akinyi) had her youngest vaccinated, that baby never got malaria," Oyoya said at a clinic as she waited to get her nine-month-old boy vaccinated in the Lake Victoria region.
"So I decided to bring mine too so that he would be malaria free."
- Game changer -
Health clinics in western Kenya -- where paediatric wards full of children sickened by malaria are not uncommon -- are starting to see results.
Admissions for malaria are falling, as is the severity of symptoms.
"Since we started administering the malaria vaccine in September 2019, we have seen a reduction of the cases of malaria," said Elsa Swerua, head nurse for malaria at Akala Health Center in Siaya County.
"Even the children who get malaria, it is not severe, and the number of deaths out of malaria has also gone down."
Less malaria -- the same person can suffer many episodes of the disease every year -- means fewer trips to the hospital, a boon for families who struggle to pay for treatment again and again.
"Before the vaccine... we would spend a lot of money on treatment and buying and going to the hospital. The cost was high," Akinyi said.
Now, there is more money to go around for food and other essentials, she said.
Dr Simon Kariuki, chief research officer at the Kenya Medical Research Institute, and a leading expert on malaria, said the vaccine was a game changer.
"We showed that this vaccine is safe, and can be given to young African children who bare the higher burden of malaria," he said.
The pilot trial had shown the vaccine could "reduce malaria incidents in young children in these areas by almost 40 percent", he said.
The WHO has recommended that the vaccine be administered in a four-dose regimen for children from five months of age in areas with moderate to high transmission of malaria.
S.Janousek--TPP