SCS
0.0200

Writhing in pain on a hospital bed in a Kenyan coastal town, teenage snakebite victim Shukurani Konde Tuva faced the grim reality of his left leg from above the knee being amputated.
The 14-year-old was bitten by a puff adder -- a venomous snake and the most common snakebite in sub-Saharan Africa -- while eating outdoors in his village near the town of Malindi more than a month ago.
His family rushed him to hospital two hours away by motorbike, but the antivenom he received did not help.
"My son's leg is totally rotten and maggots are even emanating from it. They'll have to cut it," said his distraught mother, Mariamu Kenga Kalume.
Some 5.4 million people are bitten by snakes each year globally and roughly half are poisoned by venom, according to World Health Organization (WHO) data.
Up to 138,000 people die and 400,000 suffer permanent physical effects, though the WHO says the numbers are a "gross underestimation" since an estimated 70 percent of cases go unreported.
Traditional beliefs and myths skew the data as some victims turn to home-grown remedies or attribute bites to voodoo "sent by their enemies" instead of seeking medical care.
- 'Snake stone' -
A few kilometres (miles) from where Shukurani lay in pain, traditional healer Douglas Rama Bajila showed AFP the concoctions he uses to "suck out" venom.
One popular remedy is the "snake stone", made from a cow's bone and sold for about $1.
Bajila said it can be reused multiple times: it simply needs to be soaked in milk for a few hours to "recharge".
One was placed on Shukurani's leg as he was transported to hospital but unfortunately fell off along the way, his mother said.
Experts worry that by using traditional snakebite remedies, patients are losing precious time but they are popular because antivenom treatments are expensive.
Antivenoms cost up to 8,000 shillings (about $62) per vial, and some patients require as many as 20 doses.
Ruth Kintalel, 30, from a pastoralist community in Kajiado county near the capital Nairobi, said she spent over five months in hospital after a red spitting cobra bit her in her sleep.
"My husband sold our livestock to cover the rising hospital bill," said Kintalel, who is still paralysed in her right arm seven years later.
- 'Bad reactions' -
Experts say Kenya receives between 10,000 and 30,000 vials of antivenom per year and needs 100,000.
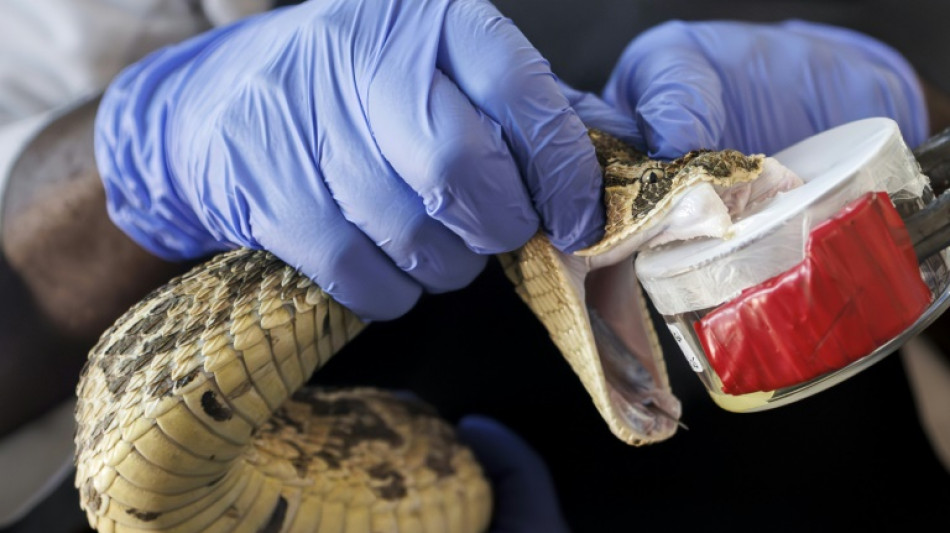
Antivenom is made by "milking" venom from the fangs of snakes, which is then diluted and injected in small doses into animals such as horses, which produce antibodies that can be extracted for use in humans.
Using snakes from different regions, even of the same species, can reduce the effectiveness of the antivenom and cause "really bad reactions", said Kyle Buster Ray, a curator at the Watamu Snake Farm on the Kenyan coast.
Kenya's stock of antivenom is not always effective because much comes from other countries like India, he said.
His farm houses over 400 venomous and non-venomous snakes and seeks to re-establish faith in antivenom that has been undermined by too many shoddy treatments.
It offers free antivenom to critical cases locally, but stocks are limited.
The farm also trains communities in life-saving snakebite responses.
During a session attended by AFP, about half the community said they had been bitten at least once, and nearly all had initially turned to traditional medicines.
Many showed signs of paralysis, with one suffering partial blindness.
- 'Trauma' -
In Nairobi, the Snakebite Research and Intervention Centre within the Kenya Institute of Primate Research is working on an antivenom specific to the country and applicable to multiple species.
Valentine Musabyimana, a research fellow at the institute, said they "are aiming for an antivenom where a patient will require only one vial with great potency".
Government subsidies should make it affordable, she hopes, though it is expected to take about two years before the antivenom is available.
That is too late for 14-year-old Shukurani.
At the snake farm, Ray warned that the boy faced psychological as well as physical consequences.
"Someone has watched their limb completely rot... there's a lot of mental trauma," Ray said.
K.Pokorny--TPP