SCS
0.0200

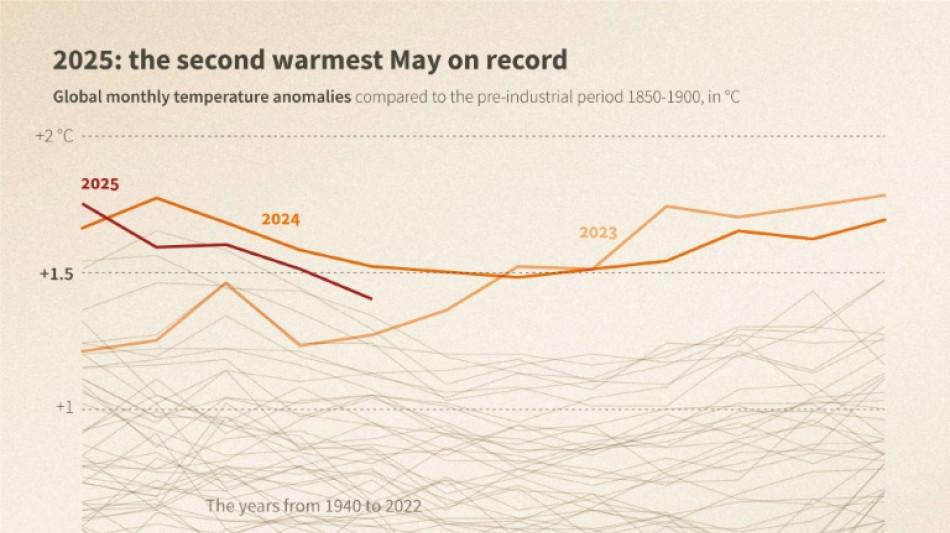
Global heating continued as the new norm, with last month the second warmest May on record on land and in the oceans, according to the European Union's climate monitoring service.
The planet's average surface temperature dipped below the threshold of 1.5 degree Celsius above preindustrial levels, just shy of the record for May set last year, according to the Copernicus Climate Change Service.
The same held for the world's oceans. With a surface temperature of 20.79C, last month was second only to May 2024, with some unprecedented warmth regionally.
"Large areas in the northeast North Atlantic, which experienced a marine heatwave, had record surface temperatures for the month," Copernicus reported. "Most of the Mediterranean Sea was much warmer than average."
The increasingly dire state of the oceans is front-and-centre at the third UN Ocean Conference (UNOC), which kicked off Monday in Nice, France.
Ocean heatwaves are driving marine species to migrate, damaging ecosystems, and reducing the ability of ocean layers to mix, thus hindering the distribution of nutrients.
Covering 70 percent of the globe's surface, oceans redistribute heat and play a crucial role in regulating Earth's climate.
Surface water warmed by climate change drive increasingly powerful storms, causing new levels of destruction and flooding in their wake.
Some parts of Europe, meanwhile, "experienced their lowest levels of precipitation and soil moisture since at least 1979," Copernicus noted.
Britain has been in the grips of its most intense drought in decades, with Denmark and the Netherlands also suffering from a lack of rain.
- 'Brief respite' -
Earth's surface last month was 1.4C above the preindustrial benchmark, defined as the average temperature from 1850 to 1900, before the massive use of fossil fuels caused the climate to dramatically warm.
"May 2025 interrupts an unprecedentedly long sequence of months above 1.5C," noted Carlo Buontempo, director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service.
All but one of the previous 22 months crossed this critical threshold, which marks the 2015 Paris Agreement's most ambitious target for capping global warming.
"This may offer a brief respite for the planet, but we expect the 1.5C threshold to be exceeded again in the near future due to the continued warming of the climate system," he added.
Over the 12-month period June 2024 to May 2025, warming averaged 1.57C compared to the 1850-1900 benchmark.
The Paris treaty target, however, is pegged to a 20-year average, in order to account for the influence of natural variability.
The UN's climate science advisory panel, the IPCC, has said there's a 50-percent change of breaching the 1.5C barrier in line with these criteria between 2030 and 2035.
Using this method of calculation, the world today has warmed by at least 1.3C.
The UN's World Meterological Organization (WMO), meanwhile, has said there's a 70 percent chance the five-year period 2025-2029, on average, will exceed the 1.5C limit.
Scientists stress the importance of limiting global warming as soon and as much as possible because every fraction of a degree increases the risks of more deadly and destructive impacts, on land and in the sea.
Limiting warming to 1.5C rather than 2C would significantly reduce the most catastrophic consequences, the IPCC concluded in a major report in 2018.
J.Marek--TPP