SCS
0.0200

The ozone layer that shields life on Earth from deadly solar radiation is on track to recover within decades, but controversial geoengineering schemes to blunt global warming could reverse that progress, a major scientific assessment warned Monday.
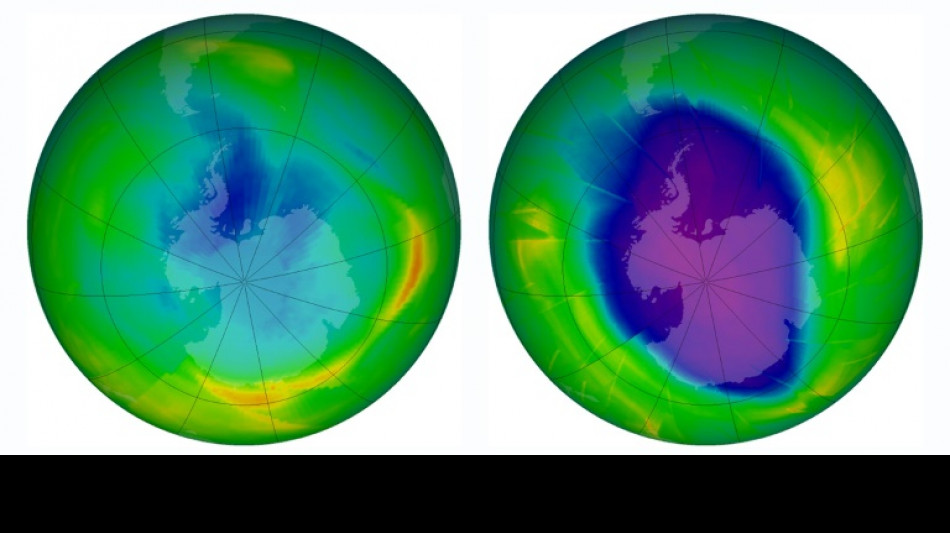
Since the mid-1970s, certain industrial aerosols have led to the depletion of ozone in the stratosphere, 11 to 40 kilometres (7 to 25 miles) above Earth's surface.
In 1987, nearly 200 nations agreed on the Montreal Protocol to reverse damage to the ozone layer by banning chemicals that destroy this naturally occurring stratum of molecules in the atmosphere.
That agreement is working as hoped, and is in line with previous projections, more than 200 scientists found.
"Ozone is recovering, this is a good story," John Pyle, a professor at the University of Cambridge and co-chair of Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion, told AFP.
The ozone layer should be restored -- both in area and depth -- by around 2066 over the Antarctic region, where ozone depletion has been most pronounced, according to the report, jointly released by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the UN Environment Programme, and government agencies in the US and the European Union.
Over the Arctic, full recovery will happen around 2045, and for the rest of the world in about 20 years.
An intact ozone layer filters out most of the Sun's short-wave ultraviolet radiation, which damages DNA in living organisms and can cause cancer.
At ground level, however, ozone is a major component of air pollution and exacerbates respiratory disease.
Efforts to repair the ozone layer intersect with the fight against global warming.
- Like a volcano -
The phase-out of ozone-depleting substances -- some of them powerful greenhouse gases -- will have avoided up to one degree Celsius of warming by mid-century compared to a scenario in which their use expanded some three percent per year, according to the assessment.
A class of industrial aerosols developed to replace those banned by the Montreal Protocol also turned out to be powerful greenhouse gases, and will be phased out over the next three decades under a recent amendment to the 1987 treaty.
But while the world pulled together to tackle the damage to the ozone layer, it has failed to curb carbon emissions quickly enough to forestall dangerous warming.
A world barely 1.2C above pre-industrial levels has already been buffeted by record heatwaves, droughts and temperatures, and is headed for a disastrous 2.7C above that benchmark.
With emissions continuing to rise and time running out to avoid some of the worst impacts, controversial geoengineering schemes are moving to the centre of climate change policy debates.
These include proposals to blunt global warming by depositing sulphur particles into the upper atmosphere.
But the report cautioned this could sharply reverse the recovery of the ozone layer.
So-called stratospheric aerosol injection (SAI) is increasingly seen as a potential stop-gap measure for capping temperatures long enough to tackle the problem at the source.
Nature demonstrates that it works: the violent 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines -- which spewed millions of tonnes of dust and debris -- lowered global temperatures for about a year.
- Unintended consequences -
Scientists calculate that injecting 8 to 16 million tonnes of sulphur dioxide into the stratosphere each year, roughly equivalent to Pinatubo's output, would cool Earth's temperature by about 1C.
Simulations over Antarctica in October -- when the ozone hole is biggest -- show that so-called stratospheric aerosol injection over 20 years would lower global temperatures by 0.5C.
But there's a trade-off: the ozone layer would be reduced to its 1990 levels, only a third of what it was before the impact of human activity.
The world would see "a continuing severe depletion of ozone while such solar radiation management continues," Pyle said.
The UN's climate science advisory panel, the IPCC, has warned of other unintended consequences, ranging from the disruption of African and Asian monsoons, upon which hundreds of millions depend for food, to a drying of the Amazon, which is already transitioning toward a savannah state.
The new report, the 10th to date, also highlights an unexpected decline of ozone in the lower stratosphere over the planet's populated tropical and mid-latitude regions.
Up to now, chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs, and other molecules have mainly eroded ozone in the upper stratosphere, and over the poles.
Scientists are investigating two possible culprits: industrial chemicals not covered by the Montreal Protocol called "very short-lived substances" (VSLSs), and climate change.
O.Ruzicka--TPP