CMSC
-0.1050

Those lucky enough to have seen them will never forget.
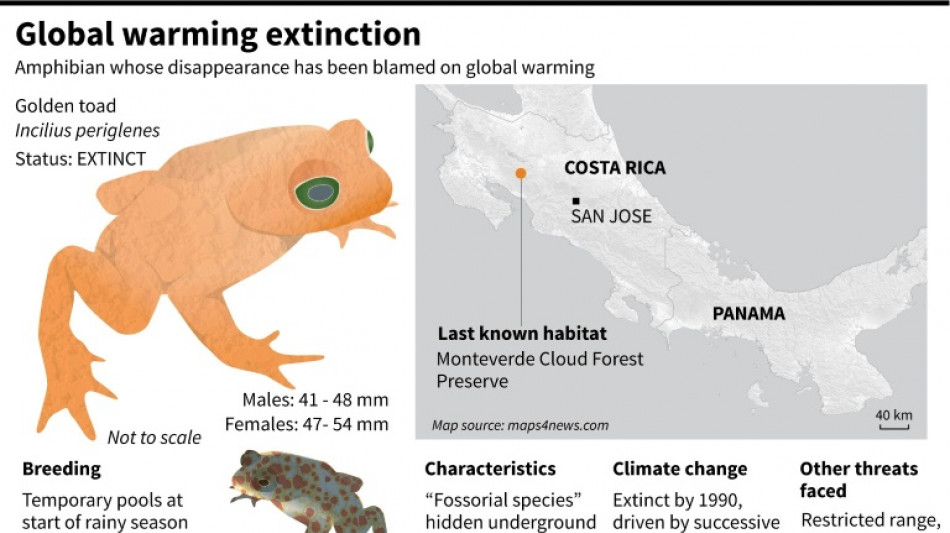
For just a few days every year, the elfin cloud forest of Costa Rica came alive with crowds of golden toads the length of a child's thumb, emerging from the undergrowth to mate at rain-swelled pools.
In this mysterious woodland the cloud drapes over mountain ridges and "the trees are dwarfed and wind-sculpted, gnarled and heavily laden with mosses," said J Alan Pounds, an ecologist at the Monteverde Cloud Forest Preserve in Costa Rica.
"The soils are very dark and so golden toads would stand out like animal figurines. It was quite a spectacle."
Then in 1990, they were gone.
The golden toad was the first species where climate change has been identified as a key driver of extinction.
Its fate could be just the beginning.
For years, researchers have warned that the world is facing both a climate and a biodiversity crisis. Increasingly they say they are connected.
- One in 10 face extinction -
Even if warming is capped at the ambitious target of 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, the UN's Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change says nearly one in 10 of all species face an extinction threat.
The golden toad was only found in Monteverde's highland forest. So when trouble hit, the species was completely wiped out.
"It was pretty clear about 99 percent of the population declined within a single year," said Pounds, whose research into the disappearance of the golden toad was cited in the IPCC's February report on climate impacts.
Climate change was barely on the research radar when Pounds first arrived in Costa Rica in the early 1980s to study amphibians.
But global warming was already beginning to take its toll.
After the disappearance of the golden toad, the Monteverde harlequin frog and others, researchers compared datasets on temperature and weather patterns with those on local species.
They found not only the signature of the periodic El Nino weather phenomenon, but also trends linked to changes in climate.
- Climate 'trigger' -
The die-offs occurred after unusually warm and dry periods.
Pounds and his colleagues linked the declines to chytridiomycosis infection, but concluded that disease was only the "bullet -- climate change was pulling the trigger.
"We hypothesised that climate change and resultant extreme events were somehow loading the dice for these kinds of outbreaks," Pounds told AFP.
It was not an isolated incident.
The expansion of the chytrid fungus globally, along with local climate change "is implicated in the extinction of a wide range of tropical amphibians," according to the IPCC.
The fingerprints of global warming have since been seen in other disappearances.
The Bramble Cay melomys, a small rodent living on a low-lying island in the Torres Strait, was last seen in 2009.
The only mammal endemic to the Great Barrier Reef, its populations were battered by sea-level rise, increased storm surges and tropical cyclones -- all made worse by climate change.
Vegetation that provided its food plummeted from 11 plant species in 1998 to just two in 2014. It was recently declared extinct.
Today, climate change is listed as a direct threat to 11,475 species assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. Around 5,775 are at risk of extinction.
- #MeToo for species -
The main reason why climate change is increasingly cited as a threat to so many species is that its impacts are becoming more obvious, said Wendy Foden, the head of the IUCN's climate change specialist group.
But there is also a growing understanding of the enormous variety of effects.
Beyond extreme weather, warming can also cause species to move, change behaviour or even skew to having more male or female offspring.
And that's on top of other human threats like poaching, deforestation, overfishing and pollution.
In 2019, a report by UN biodiversity report experts said one million species could disappear in the coming decades, raising fears that the world is entering a sixth era of mass extinction.
"It's absolutely terrifying," said Foden, adding that warnings of catastrophic biodiversity loss have often been overlooked.
"We need a #MeToo movement for species, a whole wake up on what we are doing."
Almost 200 countries are currently locked in global biodiversity talks to try to safeguard nature, including a key milestone of 30 percent of Earth's surface protected by 2030.
But Foden said the threat of climate change means that the response will have to go beyond traditional conservation.
"That can't happen anymore, even in the most remote wilderness, climate change will affect it," Foden said.
In some cases, people will need to choose which species to save.
Take the endangered African penguin in South Africa, which Foden wrote about for the IPCC report on climate impacts.
Forced to nest in the open after humans mined their guano nesting sites, the adults now have to swim ever further to find fish, likely because of a combination of overfishing and climate change. Meanwhile, the chicks in exposed nests can die from heat stress.
"We are down to the last 7,000 breeding pairs. At this point, every penguin counts," Foden said.
- Cloudless forest -
In Monteverde, even the clouds have changed.
While rainfall has increased somewhat over the past 50 years, Pounds said it has become much more variable.
In the 1970,s the forest saw around 25 dry days a year on average -- in the last decade it has been more like 115.
The mist that used to keep the forest wet during the dry season has reduced by around 70 percent.
Pounds said sometimes tourists in the area stop him and ask directions to the Cloud Forest.
"And I say: 'You're in it,'" he said.
"It often feels more like a dust forest than a cloud forest."
Researchers have also seen steep declines in frogs, snakes and lizards and changes in the bird populations. Some have moved uphill to cooler areas, others have vanished from the area completely.
As for the golden toad, last year a team from the Monteverde Conservation League, supported by the conservation group Re:wild, launched an expedition to look for the golden toad in its historic habitat in the Children's Eternal Rainforest, after tantalising rumours of sightings.
But in vain.
Meanwhile, Pounds and his colleagues continue to keep an eye out for the golden toad during the rainy season.
"We haven't completely given up," he said.
"But with each passing year, it looks less likely that they're going to reappear."
X.Vanek--TPP