RBGPF
0.1000

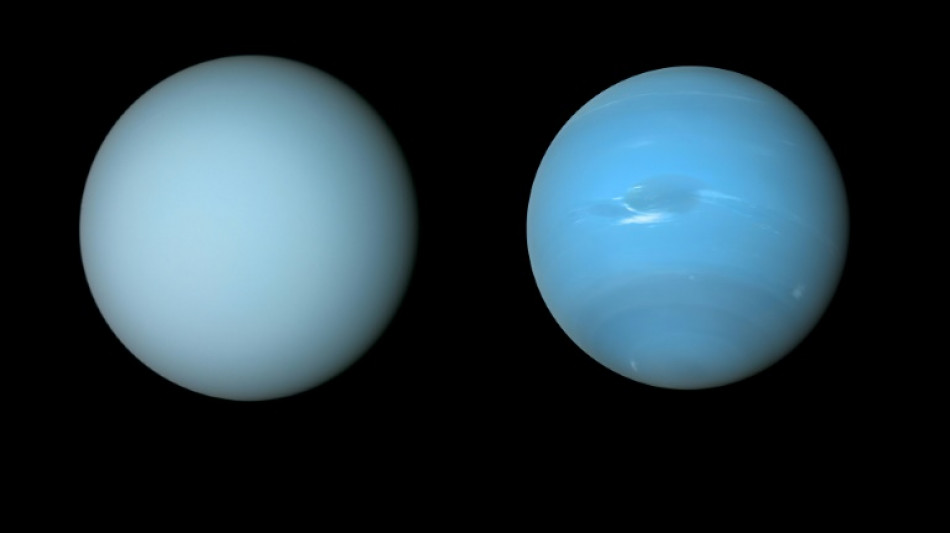
It could be raining diamonds on planets throughout the universe, scientists suggested Friday, after using common plastic to recreate the strange precipitation believed to form deep inside Uranus and Neptune.
Scientists had previously theorised that extremely high pressure and temperatures turn hydrogen and carbon into solid diamonds thousands of kilometres below the surface of the ice giants.
Now new research, published in Science Advances, inserted oxygen into the mix, finding that "diamond rain" could be more common than thought.
Ice giants like Neptune and Uranus are thought to be the most common form of planet outside our Solar System, which means diamond rain could be occurring across the universe.
Dominik Kraus, a physicist at Germany's HZDR research lab and one of the study's authors, said that diamond precipitation was quite different to rain on Earth.
Under the surface of the planets is believed to be a "hot, dense liquid", where the diamonds form and slowly sink down to the rocky, potentially Earth-size cores more than 10,000 kilometres (6,200 miles) below, he said.
There fallen diamonds could form vast layers that span "hundreds of kilometres or even more", Kraus told AFP.
While these diamonds might not be shiny and cut like a "a nice gem on a ring", he said they were formed via similar forces as on Earth.
Aiming to replicate the process, the research team found the necessary mix of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a readily available source -- PET plastic, which is used for everyday food packaging and bottles.
Kraus said that while the researchers used very clean PET plastic, "in principle the experiment should work with Coca-Cola bottles".
The team then turned a high-powered optical laser on the plastic at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California.
"Very, very short X-ray flashes of incredible brightness" allowed them to watch the process of nanodiamonds -- tiny diamonds too small to see with the naked eye -- as they formed, Kraus said.
"The oxygen that is present in large amounts on those planets really helps suck away the hydrogen atoms from the carbon, so it's actually easier for those diamonds to form," he added.
- New way to make nanodiamonds? -
The experiment could point towards a new way to produce nanodiamonds, which have a wide and increasing range of applications including drug delivery, medical censors, non-invasive surgery and quantum electronics.
"The way nanodiamonds are currently made is by taking a bunch of carbon or diamond and blowing it up with explosives," said SLAC scientist and study co-author Benjamin Ofori-Okai.
"Laser production could offer a cleaner and more easily controlled method to produce nanodiamonds," he added.
The diamond rain research remains hypothetical because little is known about Uranus and Neptune, the most distant planets in our Solar System.
Only one spacecraft -- NASA's Voyager 2 in the 1980s -- has flown past the two ice giants, and the data it sent back is still being used in research.
But a NASA group has outlined a potential new mission to the planets, possibly launching next decade.
"That would be fantastic," Kraus said.
He said he is greatly looking forward to more data -- even if it takes a decade or two.
I.Mala--TPP