RBGPF
0.1000

The James Webb and Hubble telescopes on Thursday revealed their initial images of a spacecraft deliberately crashing into an asteroid, marking the first time the two most powerful space telescopes have observed the same celestial object.
The world's telescopes turned their gaze towards the space rock Dimorphos earlier this week for a historic test of Earth's ability to defend itself against a potential future life-threatening asteroid.
Astronomers rejoiced as NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) impactor slammed into its pyramid-sized target 11 million kilometres (6.8 million miles) from Earth on Monday night.
Images taken by Earth-bound telescopes showed a vast cloud of dust expanding out of Dimorphos -- and its big brother Didymos which it orbits -- after the spacecraft hit.
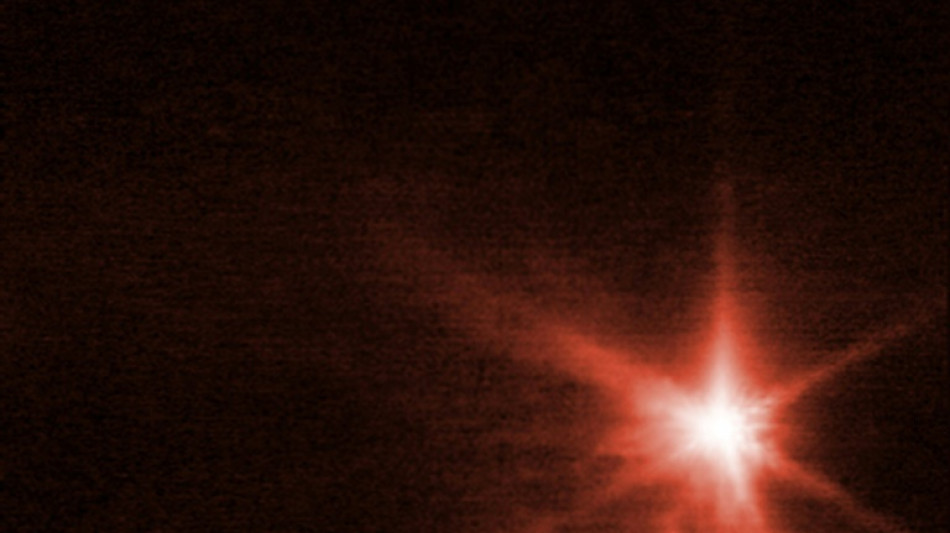
While those images showed matter spraying out over thousands of kilometres, the James Webb and Hubble images "zoom in much closer", said Alan Fitzsimmons, an astronomer at Queen's University Belfast involved in observations with the ATLAS project.
James Webb and Hubble can see "within just a few kilometres of the asteroids and you can really clearly see how the material is flying out from that explosive impact by DART", Fitzsimmons told AFP.
"It really is quite spectacular," he said.
Observations from the space telescopes will help reveal how much -- and how quickly -- matter sprayed from the asteroid, as well as the nature of its surface.
- 'A beautiful demonstration' -
An image taken by James Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) four hours after impact shows "plumes of material appearing as wisps streaming away from the centre of where the impact took place", according to a joint statement from the European Space Agency, James Webb and Hubble.
James Webb's images were shown in red because the telescope operates primarily in the infrared spectrum, which allows it to peer further into the universe than ever before.
The images from Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 were blue because it shows the impact on visible light.
Hubble images from 22 minutes, five hours and eight hours after impact show the expanding spray of matter from where DART hit on the asteroid's left.
The true measure of DART's success will be exactly how much it diverted the asteroid's trajectory, so the world can start preparing to defend itself against bigger asteroids that could head our way in the future.
However, it will take Earth-bound telescopes and radar days or even weeks to work out exactly where Dimorphos is, compared to where it would have been.
Measurements using that data will probably start next week, Fitzsimmons said.
"The problem we have at the moment is that there's still a lot of dust and debris around the asteroids," he said.
"How quickly astronomers can make that measurement will depend on exactly how efficient DART was," he added. The more the asteroid has been knocked off course, the easier it will be to measure.
Since launching in December and releasing its first images in July, James Webb has taken the title of most powerful space telescope from Hubble.
With astronomers lined up for precious time to peer into the universe, the DART test is the first time both telescopes have observed the same event.
Fitzsimmons said the images were "a beautiful demonstration of the extra science you can get by using more than one telescope simultaneously".
Y.Havel--TPP