RBGPF
0.1000

Scientists have successfully implanted and integrated human brain cells into newborn rats, creating a new way to study complex psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and autism, and perhaps eventually test treatments.
Studying how these conditions develop is incredibly difficult -- animals do not experience them like people, and humans cannot simply be opened up for research.
Scientists can assemble small sections of human brain tissue derived from stem cells in petri dishes, and have already done so with more than a dozen brain regions.
But in dishes, "neurons don't grow to the size which a human neuron in an actual human brain would grow", said Sergiu Pasca, the study's lead author and professor of psychiatry and behavioural sciences at Stanford University.
And isolated from a body, they cannot tell us what symptoms a defect will cause.
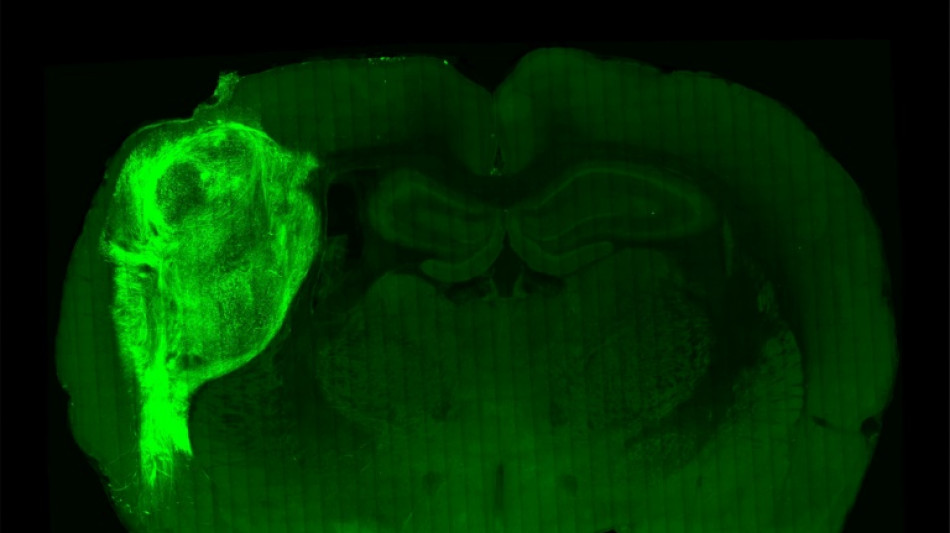
To overcome those limitations, researchers implanted the groupings of human brain cells, called organoids, into the brains of young rats.
The rats' age was important: human neurons have been implanted into adult rats before, but an animal's brain stops developing at a certain age, limiting how well implanted cells can integrate.
"By transplanting them at these early stages, we found that these organoids can grow relatively large, they become vascularised (receive nutrients) by the rat, and they can cover about a third of a rat's (brain) hemisphere," Pasca said.
- Ethical dilemmas -
To test how well the human neurons integrated with the rat brains and bodies, air was puffed across the animals' whiskers, which prompted electrical activity in the human neurons.
That showed an input connection -- external stimulation of the rat's body was processed by the human tissue in the brain.
The scientists then tested the reverse: could the human neurons send signals back to the rat's body?
They implanted human brain cells altered to respond to blue light, and then trained the rats to expect a "reward" of water from a spout when blue light shone on the neurons via a cable in the animals' skulls.
After two weeks, pulsing the blue light sent the rats scrambling to the spout, according to the research published Wednesday in the journal Nature.
The team has now used the technique to show that organoids developed from patients with Timothy syndrome grow more slowly and display less electrical activity than those from healthy people.
The technique could eventually be used to test new drugs, according to J. Gray Camp of the Roche Institute for Translational Bioengineering, and Barbara Treutlein of ETH Zurich.
It "takes our ability to study human brain development, evolution and disease into uncharted territory", the pair, who were not involved in the study, wrote in a review commissioned by Nature.
The method raises potentially uncomfortable questions -- how much human brain tissue can be implanted into a rat before the animal's nature is changed? Would the method be ethical in primates?
Pasca argued that limitations on how deeply human neurons integrate with the rat brain provide "natural barriers".
Rat brains develop much faster than human ones, "so there's only so much that the rat cortex can integrate".
But in species closer to humans, those barriers might no longer exist, and Pasca said he would not support using the technique in primates for now.
He argued though that there is a "moral imperative" to find ways to better study and treat psychiatric disorders.
"Certainly the more human these models are becoming, the more uncomfortable we feel," he said.
But "human psychiatric disorders are to a large extent uniquely human. So we're going to have to think very carefully... how far we want to go with some of these models moving forward."
C.Novotny--TPP